"Complete intelligence is not always available in a perfect manner. Even incomplete intelligence, if assessed properly and promptly by experts and acted upon effectively, can make a difference."
Intelligence Fun Fact:
The Role of Intelligence Analysts in Modern Media Organizations
In the rapidly evolving landscape of media, where information is disseminated at an unprecedented pace, media organizations are increasingly turning to intelligence analysts to navigate the complex web of data, assess risks, and make informed decisions. This essay explores the multifaceted role of intelligence analysts in modern media organizations, examining how these professionals contribute to shaping news narratives, mitigating risks, and enhancing overall media strategy.
Understanding Intelligence Analysis in Media:
Intelligence analysis in media involves the systematic collection, evaluation, and interpretation of information to provide actionable insights. While traditionally associated with government agencies, intelligence analysis has found a new home in media organizations seeking to stay ahead in a highly competitive and dynamic industry.
Information Gathering and Verification: One of the primary responsibilities of intelligence analysts in media is to gather and verify information. In an era where misinformation and fake news proliferate, these analysts play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and credibility of the content being disseminated. They leverage various tools— including open-source intelligence and data analytics—to sift through vast amounts of information and identify reliable sources.
Risk Assessment: Media organizations operate in a volatile environment where reputational risks are omnipresent. Intelligence analysts assess potential risks associated with stories, sources, or geopolitical events that might impact the organization. By conducting thorough risk assessments, they empower decision-makers to make informed choices about whether to pursue a particular story, engage with a specific source, or cover a sensitive topic.
Audience Analysis: Understanding the audience is paramount for media organizations, and intelligence analysts contribute by providing insights into audience preferences, behaviors, and demographics. By analyzing audience data, these professionals help tailor content to specific target groups, ensuring that the media organization remains relevant and resonates with its audience.
Competitive Intelligence: In the highly competitive media landscape, staying ahead of rivals is crucial. Intelligence analysts monitor the activities of competitors, analyzing their strategies, content, and audience engagement. This competitive intelligence enables media organizations to identify trends, capitalize on opportunities, and differentiate themselves in a crowded market.
Crisis Management: Media organizations are not immune to crises. Reputational damage, cybersecurity threats, or unforeseen events could require crisis management. Intelligence analysts play a pivotal role in developing crisis management strategies by anticipating potential crises, monitoring online sentiment, and providing real-time analysis during unfolding events. Their insights enable media organizations to respond swiftly and effectively, minimizing damage to their reputation.
Cybersecurity: With the increasing digitization of media operations, cybersecurity has become a critical concern. Intelligence analysts in media organizations are tasked with monitoring and mitigating cybersecurity threats, safeguarding sensitive information, and ensuring the integrity of digital platforms. Their role extends beyond traditional journalism to protect the organization's digital assets and maintain trust with audiences.
Policy and Regulatory Compliance: Media organizations operate within a complex web of legal and regulatory frameworks. Intelligence analysts assist in navigating these complexities by staying abreast of changes in laws and regulations that may impact the industry. This proactive approach ensures that media organizations can adapt to evolving legal landscapes while maintaining ethical standards in their reporting.
To wrap up, the integration of intelligence analysts into media organizations is more of a strategic response to the challenges posed by the fast-paced and competitive nature of the industry. These professionals contribute significantly to the success of media organizations by providing valuable insights, managing risks, and enhancing decision-making processes. As the media landscape continues to evolve, the role of intelligence analysts is likely to become even more integral to the success and sustainability of modern media organizations.
Stay safe out there!
Comprehensive Analysis of the Biden-Xi Summit
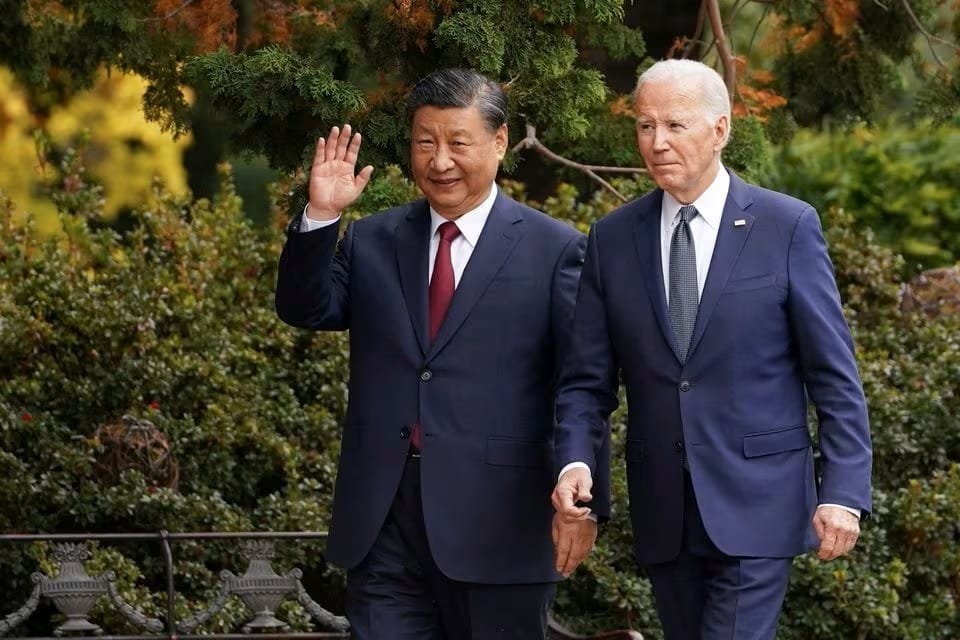

The recent summit between leaders of the United States and China has emerged as a pivotal event in the ongoing saga of geopolitical relations. The event unfolded against a backdrop of heightened tensions and complex diplomatic challenges. This high-stakes meeting, marked by a notable shift in tone and demeanor, has the potential to reshape the geopolitical landscape and influence global dynamics in unforeseen ways.
As intelligence professionals dissect the intricacies of this summit, it becomes imperative to delve into the background of U.S.-China relations, explore the key highlights of the summit, and conduct a comprehensive analysis of its geopolitical implications. This intelligence update aims to unravel the nuances surrounding the summit, decipher who stands to benefit the most, examine the rhetoric and posturing of both nations, and forecast the potential trajectories of an ever-evolving geopolitical landscape.
The geopolitical landscape leading up to the U.S.-China summit had been fraught with tensions, reaching a level not seen in over five decades. President Joe Biden's meeting with his Chinese counterpart, President Xi Jinping, unfolded against a backdrop of hostilities, exacerbated by contentious issues such as China's claims over Taiwan, disputes in the South China Sea, and U.S. export bans on advanced technology. The deterioration of diplomatic relations hit a new low following an incident involving the notorious Chinese spy balloon and China's subsequent severing of military communications. These events amplify concerns of potential miscalculations in the Asia-Pacific region.
Amid these challenges, both nations faced compelling incentives to engage in dialogue. The Biden administration, aware of the risks posed by the proximity of U.S. and Chinese forces in the Indo-Pacific, sought to avoid escalating tensions that could result in a global crisis during Biden's upcoming reelection bid. On the other side, President Xi Jinping, facing economic strife and internal political pressures, needed to assert control over vital U.S. relations while signaling a willingness to de-escalate tensions with major powers, particularly the United States.
The expectations for the summit were deliberately set low, with both leaders having much to gain from portraying the meeting as productive. The four-hour talks, aimed at addressing critical issues such as the restoration of military communications and the management of potential incidents in the South and East China seas. President Biden adopted a "trust but verify" approach, and expressed hope in rationalizing and managing the competitive relationship between the two nations, emphasizing the need to prevent conflicts.
While the summit yielded incremental progress and a sense of cautious optimism, the underlying factors driving the U.S.-China rivalry remained largely untouched. The need for constant management of this delicate relationship to prevent it from spiraling into open conflict was evident.
As the stage was set for the summit, the anticipation in the international community grew, with observers closely watching for signs of concessions and the potential recalibration of geopolitical dynamics.
Geopolitical Analysis
The U.S.-China summit marked a pivotal moment in the complex geopolitical relationship between the world's two largest economies. The outcomes of the four-hour talks and subsequent interactions provided valuable insights into the current state of affairs and the potential trajectory of future interactions. Below is a detailed geopolitical analysis of the key aspects that emerged from the summit.
A. Agreements and Incremental Progress
Military Communications and Maritime Stability:
The agreement to re-establish military-to-military contacts emerged as one of the most significant outcomes of the summit. The Biden administration's persistent efforts to restore communication channels severed by China were agreed upon. This addresses a critical national security concern. The potential for misjudgments and incidents involving U.S. and Chinese naval or air forces in the Indo-Pacific region had been a looming nightmare scenario. The resumption of military dialogues, however, is not without challenges. The success of such efforts hinges on whether the agreements made by Xi Jinping filter down to lower levels of the People's Liberation Army.
Fentanyl Cooperation:
The joint commitment to combat the flow of fentanyl from China to the United States showcased a cooperative effort to address a pressing issue. The opioid epidemic, exacerbated by the illicit production and distribution of fentanyl, has been a longstanding concern for the Biden administration. The agreement, made on a "trust but verify" basis, signaled an attempt to bridge gaps in collaboration on issues of shared interest.
B. Biden's Balancing Act and Political Risks
Domestic Political Dynamics:
President Biden's decision to engage in summit talks with President Xi Jinping faced scrutiny and criticism from domestic political opponents. The delicate balancing act between pursuing diplomatic initiatives and addressing concerns about appeasement highlighted the challenges faced by the Biden administration. The summit's success, then, was measured not only by tangible outcomes but also by its impact on Biden's political standing and the narrative surrounding U.S.-China relations in the lead-up to his reelection bid.
"Dictator" Remark:
Biden's reiterated characterization of Xi Jinping as a "dictator" reinforced the enduring challenges in the U.S.-China relationship. The remark, echoing a previous statement from June, received a strong rebuke from China's foreign ministry. They labeled it as "extremely wrong" and "irresponsible political manipulation." The diplomatic fallout from such statements adds complexity to the efforts of both nations to build trust and understanding.
C. Xi Jinping's Calculations and Domestic Pressures
Economic Struggles and Foreign Investment:
Xi Jinping's visit to the United States occurred in the context of economic challenges in China. A stagnant economy, a collapsing housing market, and rising youth unemployment created a compelling incentive for Xi to present a positive image and reassure foreign investors. The shift in China's tone, marked by a temporary pause in anti-U.S. rhetoric and emphasis on cooperation, reflected Xi's strategic move to stabilize the economic situation and attract foreign investments.
Taiwan and "One China" Policy:
The summit provided a platform for Xi Jinping to seek reaffirmation from President Biden on the "One China" policy. Xi emphasized that Taiwan is an integral part of China. The issue of Taiwan remains a thorny point in U.S.-China relations, and Xi's call for the U.S. to stop arming Taiwan and support China's "peaceful reunification" highlighted the enduring complexities in cross-strait dynamics.
D. The Perception Game and Public Diplomacy
Media Portrayals and Optics:
The carefully curated images and narratives surrounding the summit, both in Chinese state media and on social media platforms, are aimed at shaping public perceptions. The emphasis on warm welcomes, cordial walks, and positive interactions between the leaders served the dual purpose of projecting stability in the relationship to domestic audiences and managing international perceptions.
Public Reaction and Social Media Trends:
Social media platforms, particularly in China, became arenas for public reactions and discussions related to the summit. Hashtags such as #Planet-Earth-Is-Big-Enough-For-Both-China-And-The-US trended, reflecting public sentiments and interpretations of the outcomes. The attention given to personal details, such as the exchange of gifts and the leaders' interactions, contributed to shaping the narrative surrounding the summit.
E. Future Implications and Unresolved Issues
Long-Term Trajectory:
While the summit offered a temporary respite and incremental progress, the underlying factors driving the U.S.-China rivalry remain unaddressed. The trajectory of the relationship is likely to continue. This will require meticulous management to prevent further deterioration. The potential for misjudgments, the unresolved Taiwan issue, and the fundamental differences in geopolitical visions present ongoing challenges that extend beyond the immediate outcomes of the summit.
Global Power Dynamics:
The summit unfolded amid evolving global power dynamics. The Biden administration's acknowledgment of China as the only competitor with the intent and power to reshape the international order underscores the broader geopolitical context. As China and the U.S. navigate their relationship, the implications extend beyond bilateral dynamics, influencing regional and global power structures.
Challenges and Unresolved Issues
While the U.S.-China summit showcased moments of diplomatic breakthrough and cooperative agreements, several challenges and unresolved issues persist, casting a shadow over the prospect of long-term stability in the bilateral relationship.
A. Taiwan Tensions:
Xi's Assertiveness:
President Xi Jinping's call for the U.S. to cease arming Taiwan and support China's "peaceful reunification" highlights the persistent tensions surrounding Taiwan. Xi's assertive stance on Taiwan, a self-ruling democracy claimed by China, remains a significant point of contention. The summit did not provide a clear resolution to this long-standing issue, leaving room for future confrontations.
U.S. Position:
President Biden reaffirmed the United States' long-standing position on Taiwan, emphasizing the opposition to any unilateral changes to the status quo. The fundamental differences in the two nations' perspectives on Taiwan remain. This poses a challenge to finding common ground and potentially escalating tensions in the future.
B. "Dictator" Remark and Diplomatic Fallout:
Impact on Relations:
President Biden's characterization of Xi Jinping as a "dictator" during the solo press conference introduced a diplomatic strain. The strong opposition from China's foreign ministry reflects the sensitivity of personal remarks on leaders in diplomatic discourse. The fallout from such statements may impede future diplomatic efforts and complicate the path to mutual understanding.
Domestic and International Reception:
The remark not only drew ire from Beijing but also sparked domestic debates in the United States. The divided opinions on Biden's characterization of Xi show the challenges in maintaining a cohesive national narrative on U.S.-China relations. Internationally, such statements contribute to the perception of a strained relationship, potentially impacting global attitudes toward both nations.
C. Fragile Military Communications Agreement:
Resumption on "Equality and Respect" Basis:
The agreement to resume military communications is a positive step, addressing concerns about potential misunderstandings and incidents in the Asia-Pacific region. However, the caveat of resuming dialogues "on the basis of equality and respect" introduces a potential fragility. Any perceived lack of respect could strain military-to-military relations, undermining the progress made.
U.S. Strategic Concerns:
The Biden administration's push for the resumption of military dialogues aligns with its broader strategic goals in the Indo-Pacific. However, the challenges of managing a complex relationship with China extend beyond episodic dialogues. Ensuring a sustained and meaningful engagement that addresses core security concerns is a delicate task.
D. Public Opinion Dynamics:
Social Media and National Narratives:
The summit's portrayal on social media platforms, particularly in China, reflects the nuanced dynamics of public opinion. While carefully curated narratives projected positive optics, the divergent views and debates among the public highlight the challenges in shaping national narratives that align with diplomatic objectives.
Impact on Domestic Politics:
President Biden's engagement with President Xi faced scrutiny from political opponents domestically. The intersection of diplomatic initiatives with domestic political considerations adds complexity to U.S.-China relations. Navigating a path that addresses both international diplomacy and domestic concerns requires strategic finesse.
E. Long-Term Trajectory and Global Implications:
Fundamental Differences:
The summit's outcomes, while symbolizing incremental progress, did not address the fundamental differences in geopolitical visions between the U.S. and China. These disparities extend beyond specific agreements, influencing global power dynamics and regional alliances. Managing these differences requires a nuanced approach that goes beyond episodic diplomatic engagements.
Global Impact:
As the two nations grapple with their relationship, the global impact remains significant. The acknowledgment of China as a major competitor capable of reshaping the international order positions the U.S.-China rivalry within a broader geopolitical context. The evolving power dynamics have implications for regional stability and the configuration of global alliances.
In navigating these challenges and addressing unresolved issues, both the U.S. and China face a delicate balancing act. The complexities of geopolitical dynamics require sustained efforts, strategic foresight, and a commitment to constructive dialogue to achieve lasting stability. The outcomes of the summit, while offering glimpses of cooperation, underscore the enduring complexities that define the U.S.-China relationship in the 21st century.
Future Outlook
The U.S.-China summit, despite its moments of diplomatic progress, leaves a trail of uncertainties and challenges that will significantly shape the future trajectory of bilateral relations. As both nations navigate complex geopolitical landscapes and contend with domestic and international pressures, the future outlook remains nuanced and multifaceted.
A. Diplomatic Crossroads:
Strategic Reassessment:
The summit marks a strategic reassessment in both Washington and Beijing, where leaders grapple with the question of whether the U.S. and China can coexist as rivals or find common ground as partners. The nuanced diplomatic language from both sides suggests a delicate balancing act, with each nation seeking to assert its interests without derailing the fragile progress made.
Impact on Global Alliances:
The evolving dynamics between the U.S. and China reverberate across the global stage, impacting regional alliances and international cooperation. As both nations recalibrate their positions, traditional alliances face the challenge of adapting to a geopolitical landscape where U.S.-China competition defines the contours of global influence.
B. Economic Considerations:
Trade and Economic Cooperation:
The summit's outcomes show the intricate dance between economic cooperation and strategic competition. While agreements on fentanyl, military communications, and AI represent areas of mutual interest, the unresolved economic issues, including the so-called chip wars and trade imbalances, pose ongoing challenges. The future trajectory of economic relations will be closely tied to geopolitical developments.
Investment Climate:
President Xi's invitation for global businesses to invest in China reflects a keen awareness of the economic headwinds facing the nation. The future investment climate will depend on China's commitment to addressing concerns such as intellectual property theft and data security. Global investors will scrutinize China's actions to determine the feasibility and security of investment.
C. Domestic Considerations:
Xi's Leadership and Economic Challenges:
President Xi Jinping's focus on stabilizing relations with the U.S. comes against the backdrop of economic challenges and domestic political considerations. The summit's optics, including standing ovations from the U.S. business community, serve not only diplomatic but also domestic purposes, projecting an image of strong leadership capable of managing complex international relationships.
Public Opinion Dynamics:
The reception of the summit on social media platforms offers insights into public opinion dynamics. As leaders seek to navigate diplomatic waters, understanding and shaping domestic narratives will be pivotal. Public sentiment, both in China and the U.S., will influence the latitude leaders have in pursuing diplomatic initiatives.
D. Technology and Strategic Competition:
AI and Technological Frontiers:
The agreement on AI cooperation reflects the centrality of technology in the U.S.-China rivalry. As both nations vie for technological supremacy, the contours of AI collaboration will be closely watched. The unresolved issues in the so-called chip wars signal the enduring strategic competition that extends beyond diplomatic engagements.
Innovation and National Security:
The future of U.S.-China relations will be shaped by the delicate balance between innovation, economic competition, and national security. The technology sector, including AI and advanced tech, remains a battleground where both nations seek dominance. Navigating this terrain requires detailed policies that safeguard national interests without stifling global innovation.
E. Global Impact and Multilateralism:
Reimagining Global Governance:
The U.S.-China relationship has global implications for the future of governance and multilateralism. As both nations grapple with their roles in shaping international order, the summit's outcomes provide glimpses of potential areas for collaboration. However, the unresolved issues highlight the challenges of finding common ground within a framework that accommodates diverse geopolitical visions.
Asia-Pacific Dynamics:
The summit's location in the Asia-Pacific region adds a layer of complexity to regional dynamics. The agreements on military communications and discussions around Taiwan underscore the strategic importance of the region. The evolving relationships with key players in the Asia-Pacific will be instrumental in shaping the broader geopolitical landscape.
To conclude, the recent U.S.-China Summit delved into multiple crucial topics. Responsible competition, counternarcotics efforts, addressing AI risks, and complex issues like human rights and trade were all covered. The commitment to ongoing dialogue on climate, security, and technology safety signals a recognition of shared global responsibilities. Despite differences, both nations acknowledge the necessity of continued engagement. The future of U.S.-China relations hinges on navigating complexities, rebuilding trust, and finding common ground amid the challenges. The road ahead involves a pragmatic approach to foster cooperation while acknowledging and managing differences. The summit sets the tone for an ongoing, nuanced relationship between the two major powers, with the potential for constructive collaboration in key areas.
This Week Explained

Stay safe out there